The Ear and Hearing Protection
By Johan Liljencrants [1]
The ear is a wonderful feat of our Creator that without immediate
damage
can perceive sound pressure levels from 0 to 130 dB, an impressing
power
range of 1013 = 10000000000000 times.
A central trick to achieve this big range is the Stapedius muscle
that
pulls and displaces the smallest bone in your body, Stapes, that
transfers
the sound from the eardrum to the inner ear 'microphone'. When you hear
a strong sound this muscle contracts by a reflex to pull Stapes such
that
the sound transmission to the inner ear is decreased; it acts as a
protective
'automatic volume control'.
One problem is that this muscle contraction takes time, tens of
milliseconds.
That is why gunshots are so dangerous to the ear, because with such
short
sounds there is not enough time for this mechanism to act. Also,
just because the gunshot sound is so short, you don't perceive it as
loud
as it really is, and perhaps you neglect to protect yourself for that
reason.
With extended strong sounds Stapedius can do its work, but after a
while
it is fatigued and its protective action decreases. And
correspondingly
the auditory nerve system is fatigued and you are mislead this sound is
not as loud as it really is and again you may neglect protection.
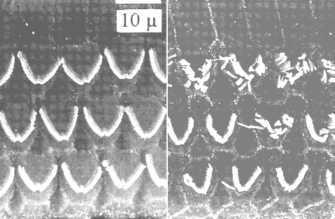 In the inner
ear, the spiral shaped Cochlea, the sound induces vibrations in the
thin
Basilar membrane which by way of a complex wave motion makes a
frequency
to place conversion. This membrane carries some 30,000 hair cells, each
with a characteristic V-shaped fence of tiny hairs like in these
pictures
[2] . The vibrations bend these hairs and this triggers the impulses to
the auditory nerves. The basic mechanism in hearing damage from
overexposure
to sound is that you wear out and crush an increasing number of these
hairs,
right picture. Once damaged they never recover and you suffer a
permanent
hearing loss. The hearing cells for high frequencies are adjacent to
the
sound input to the inner ear and these are the first ones to be
decimated
by over-exposure.
In the inner
ear, the spiral shaped Cochlea, the sound induces vibrations in the
thin
Basilar membrane which by way of a complex wave motion makes a
frequency
to place conversion. This membrane carries some 30,000 hair cells, each
with a characteristic V-shaped fence of tiny hairs like in these
pictures
[2] . The vibrations bend these hairs and this triggers the impulses to
the auditory nerves. The basic mechanism in hearing damage from
overexposure
to sound is that you wear out and crush an increasing number of these
hairs,
right picture. Once damaged they never recover and you suffer a
permanent
hearing loss. The hearing cells for high frequencies are adjacent to
the
sound input to the inner ear and these are the first ones to be
decimated
by over-exposure.
Another, and a worse, kind of damage is tinnitus, a virtual noise or
beep that goes on forever, originating in your auditory nervous system.
The cause can be infections or tumors in the inner ear, but also an
over-exposure
to sound. Tinnitus can drive people crazy.
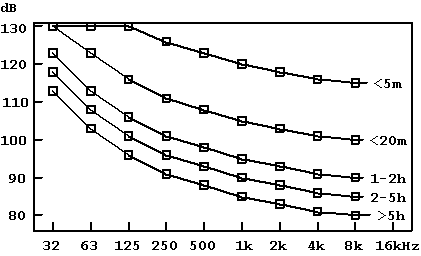 Much
research
has been done on hearing impairment induced by industrial noise and
there
are consequent international recommendations for maximal noise dose to
avoid such damage. This is a set of curves like this diagram of
maximum
permitted noise spectral level vs. frequency, sloping (very) roughly -3
dB per octave. At 500 Hz you allow 88 dB for more than 5 hours
per
day, 93 dB for 2-5 hours, 98 dB for 1-2 hours, 109 dB for less than 20
minutes per day, etc. If any of these conditions is exceeded you
should wear a noise protector.
Much
research
has been done on hearing impairment induced by industrial noise and
there
are consequent international recommendations for maximal noise dose to
avoid such damage. This is a set of curves like this diagram of
maximum
permitted noise spectral level vs. frequency, sloping (very) roughly -3
dB per octave. At 500 Hz you allow 88 dB for more than 5 hours
per
day, 93 dB for 2-5 hours, 98 dB for 1-2 hours, 109 dB for less than 20
minutes per day, etc. If any of these conditions is exceeded you
should wear a noise protector.
More recent investigations on symphony orchestra musicians have
shown
that they generally receive less hearing damage than predicted from the
sound levels they are exposed to. The reason is believed to be
psychological.
Pop musicians using amplification, and their audience, are usually way
up in the dangerous area and protectors are strongly recommended.
Also, tinnitus cases among these people are much more frequent than you
would like to know.
A typical mid-range organ flue pipe blown at 8 inches water column
and
1 foot distance roughly matches the 1-2 hour per day curve, so you
should
be able to voice such pipes without fear. Calliope and reed pipes
are considerably louder and clearly motivate protectors at close
distance.
The simplest protectors are plugs made from cotton, special fibers,
foam plastic, wax or molded plastic. Using cotton, fold a flat
pad
in two and roll it hard into a cone with its tip at the fold, put it in
your ear with the tip inward. These plugs attenuate high
frequencies
to the order of 20 dB but do very little toward low frequencies.
They do a good protection job but distort the tonal balance.
While
doing my military service we used empty pistol cartridge shells as
earplugs
(hole inwards) while shooting. Slightly uncomfortable but quite
efficient.
 To reach
more appreciable
low frequency attenuation you will need the protector type with big
cups
covering the whole ears and soft cushioned brims resting against the
head.
Lighter variants, perhaps with foam cushions stay in the 20 dB
range.
The better performance is with heavy cups and liquid filled or heavily
encapsulated cushions to insure weight and tightness as shown here;
this
type attenuates in the 30 dB range.
To reach
more appreciable
low frequency attenuation you will need the protector type with big
cups
covering the whole ears and soft cushioned brims resting against the
head.
Lighter variants, perhaps with foam cushions stay in the 20 dB
range.
The better performance is with heavy cups and liquid filled or heavily
encapsulated cushions to insure weight and tightness as shown here;
this
type attenuates in the 30 dB range.
You cannot get notably higher attenuation than this because of the
bypass
sound entering directly through your skull. For ultimate
requirements
like on an aircraft carrier you have to enclose your entire head in a
helmet,
like an astronaut.
There also exist fancy protector variants including electronics with
active noise suppression. This involves a microphone at the ear driving
a loudspeaker to counteract whatever external sound that penetrates
into
the cup. For reasons of cost and complexity this is marginally
motivated
for noise suppression alone, but is a logical add-on if you anyway want
a speaker for distraction or communication purposes.
 Plug
protectors
for musicians and other critical listeners designed for equal
attenuation
at all frequencies are exemplified in this figure showing a moderately
priced standard type that attenuates about 20 dB. The protruding taps
contain
tubes forming an acoustic filter and the soft flanges ensure tightness
to the ear canal. More elaborate special high equality types for 15 or
25 dB cost in the range of $200 and have to be individually tailored at
a hearing clinic.
Plug
protectors
for musicians and other critical listeners designed for equal
attenuation
at all frequencies are exemplified in this figure showing a moderately
priced standard type that attenuates about 20 dB. The protruding taps
contain
tubes forming an acoustic filter and the soft flanges ensure tightness
to the ear canal. More elaborate special high equality types for 15 or
25 dB cost in the range of $200 and have to be individually tailored at
a hearing clinic.
Notes
[1] Extended version of an article first appearing in Mechanical
Music
Digest 2000.01.15.
[2] Scanning electron micrographs showing about a dozen outer hair
cells
in rabbit. The three-row structure looks the same in all mammals.
Adapted
from: Borg, Conlon, Engström: Noise-induced Hearing Loss.
Scandinavian
Audiology, Vol. 24, suppl. 4, (1995).
[3] Several examples of ear protectors can be seen at
http://neatnoise.com/products.htm,
http://arbill.com/leight2.htm and
http://www.soundsafetyproducts.com/ppe/hearing/muffs/qm29.htm.
(Located by MMD editor Robbie Rhodes. No commercial connection to the
author
or the editors).
 In the inner
ear, the spiral shaped Cochlea, the sound induces vibrations in the
thin
Basilar membrane which by way of a complex wave motion makes a
frequency
to place conversion. This membrane carries some 30,000 hair cells, each
with a characteristic V-shaped fence of tiny hairs like in these
pictures
[2] . The vibrations bend these hairs and this triggers the impulses to
the auditory nerves. The basic mechanism in hearing damage from
overexposure
to sound is that you wear out and crush an increasing number of these
hairs,
right picture. Once damaged they never recover and you suffer a
permanent
hearing loss. The hearing cells for high frequencies are adjacent to
the
sound input to the inner ear and these are the first ones to be
decimated
by over-exposure.
In the inner
ear, the spiral shaped Cochlea, the sound induces vibrations in the
thin
Basilar membrane which by way of a complex wave motion makes a
frequency
to place conversion. This membrane carries some 30,000 hair cells, each
with a characteristic V-shaped fence of tiny hairs like in these
pictures
[2] . The vibrations bend these hairs and this triggers the impulses to
the auditory nerves. The basic mechanism in hearing damage from
overexposure
to sound is that you wear out and crush an increasing number of these
hairs,
right picture. Once damaged they never recover and you suffer a
permanent
hearing loss. The hearing cells for high frequencies are adjacent to
the
sound input to the inner ear and these are the first ones to be
decimated
by over-exposure.
 Much
research
has been done on hearing impairment induced by industrial noise and
there
are consequent international recommendations for maximal noise dose to
avoid such damage. This is a set of curves like this diagram of
maximum
permitted noise spectral level vs. frequency, sloping (very) roughly -3
dB per octave. At 500 Hz you allow 88 dB for more than 5 hours
per
day, 93 dB for 2-5 hours, 98 dB for 1-2 hours, 109 dB for less than 20
minutes per day, etc. If any of these conditions is exceeded you
should wear a noise protector.
Much
research
has been done on hearing impairment induced by industrial noise and
there
are consequent international recommendations for maximal noise dose to
avoid such damage. This is a set of curves like this diagram of
maximum
permitted noise spectral level vs. frequency, sloping (very) roughly -3
dB per octave. At 500 Hz you allow 88 dB for more than 5 hours
per
day, 93 dB for 2-5 hours, 98 dB for 1-2 hours, 109 dB for less than 20
minutes per day, etc. If any of these conditions is exceeded you
should wear a noise protector.
 To reach
more appreciable
low frequency attenuation you will need the protector type with big
cups
covering the whole ears and soft cushioned brims resting against the
head.
Lighter variants, perhaps with foam cushions stay in the 20 dB
range.
The better performance is with heavy cups and liquid filled or heavily
encapsulated cushions to insure weight and tightness as shown here;
this
type attenuates in the 30 dB range.
To reach
more appreciable
low frequency attenuation you will need the protector type with big
cups
covering the whole ears and soft cushioned brims resting against the
head.
Lighter variants, perhaps with foam cushions stay in the 20 dB
range.
The better performance is with heavy cups and liquid filled or heavily
encapsulated cushions to insure weight and tightness as shown here;
this
type attenuates in the 30 dB range.
 Plug
protectors
for musicians and other critical listeners designed for equal
attenuation
at all frequencies are exemplified in this figure showing a moderately
priced standard type that attenuates about 20 dB. The protruding taps
contain
tubes forming an acoustic filter and the soft flanges ensure tightness
to the ear canal. More elaborate special high equality types for 15 or
25 dB cost in the range of $200 and have to be individually tailored at
a hearing clinic.
Plug
protectors
for musicians and other critical listeners designed for equal
attenuation
at all frequencies are exemplified in this figure showing a moderately
priced standard type that attenuates about 20 dB. The protruding taps
contain
tubes forming an acoustic filter and the soft flanges ensure tightness
to the ear canal. More elaborate special high equality types for 15 or
25 dB cost in the range of $200 and have to be individually tailored at
a hearing clinic.